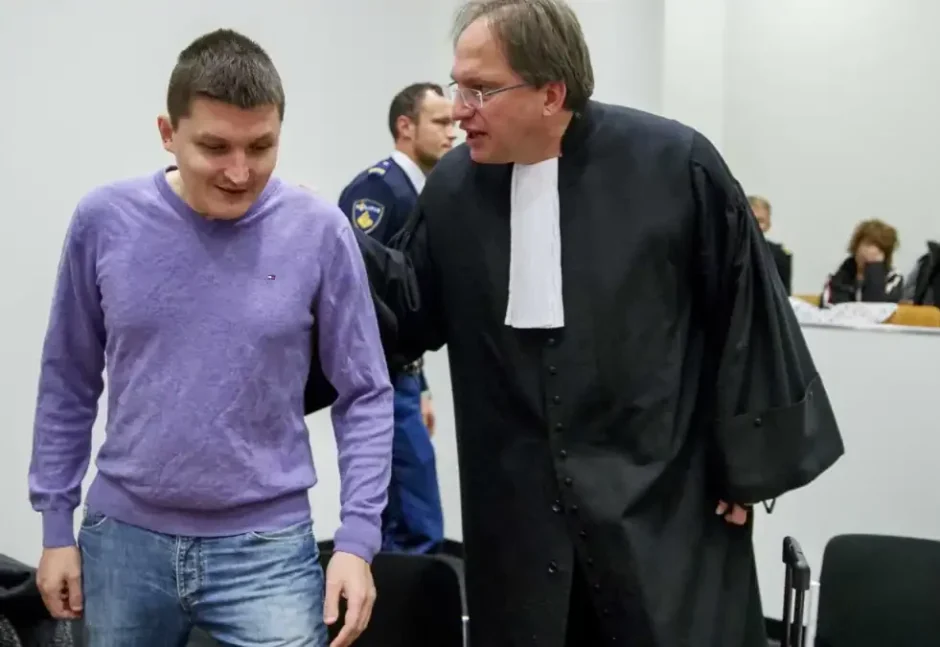
Vladimir Drinkman, a Russian Hacker was a key member of a criminal hacking group that penetrated Heartland Payment Systems. This hacking attack is considered one of the biggest data breaches of all time which ended up causing the Heartland Payment Systems more than $200 million in losses. The Russian hacker history has been released from prison after serving most of his 12-year sentence but questions are being asked as to why he got an early release after such a huge crime.
Vladimir Drinkman was released from a Pennsylvania jail on October 28, the U.S. Bureau of Prisons told RFE/RL. U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) had been turned over for deportation, a process that can take up to several months. Drinkman’s lawyer, Igor Litvak, declined to comment. RFE/RL could not immediately reach Drinkman.
Drinkman was a key member of a criminal hacking group that penetrated major U.S. corporations, including Heartland Payment Systems, which at the time it was breached in 2008 was one of the biggest U.S. payment-processing firms. The Heartland attack — the largest breach in history at the time — cost the payment company more than $200 million in losses.
Varonis, a U.S.-based cybersecurity firm, ranks the attack on Heartland among the 10 largest data breaches of all time.
Heartland also later established the Payments Processing Information Sharing Council (PPISC), which serves as a forum for banks and payment processors to share information about breaches and compliance issues, he noted. In addition to breaking into Heartland, the hacking gang also breached Nasdaq OMX Group, 7-Eleven, JC Penney, JetBlue Airways, and others, according to prosecutors. In total, they stole the data of more than 160 million credit cards, leading to more than $300 million in damages.
Greg Hunter, a Virginia-based lawyer who has represented cybercriminals from the former Soviet Union, said the Heartland case demonstrated the sophisticated evolution of Russian-speaking hackers.
“This was the beginning of specialization. Rather than an individual hacker spending a lot of time stealing credit card data and then trying to monetize it, you had guys specializing in breaching the security apparatus of a site, others selling the data.”
He went on to explain the genius behind the whole breach which made it so successful.
“The appearance of hacker forums was critical to the phenomenon of a division of labor. Hacker sites allowed these guys to find each other and work together. A guy who breaches banks could just focus on that, knowing he could find others to either help him know what to get and how to use it or just buy his services outright,”
Several of the most commonly used forums where hackers bought and sold stolen credit card data and traded tips included Cardplanet and Direct Connection. A Russian man, Aleksei Burkov, was extradited from Israel to the United States and later pleaded guilty in 2020 to U.S. charges related to his oversight of those forums.
He was deported to Russia last year.
Chuck Brooks, a cybersecurity expert and adjunct professor at Georgetown University, said the Heartland hack was a “wake-up call” for the payments and financial industries to enhance their cyber defenses. He said the breach led to stronger security policies, including a better understanding by CEOs and CFOs of the threats to business sustainability and reputation.
“After the breach, many companies added more stringent data and security policies, including encryption, multifactor authentication, and monitoring of systems and networks,”
According to U.S. court filings, Drinkman and another co-conspirator, Alexandr Kalinin, specialized in penetrating network security and gaining access to corporate data systems. Drinkman along with a third man, Roman Kotov, also focused on mining the networks to steal valuable data. Another Russian man, Dmitry Smilyanets, then sold the stolen credit card information on forums for $10 to $50 each and distributed the proceeds of the scheme to the others, according to prosecutors.
Kalinin and Kotov, both of whom are Russian citizens, are believed to still be in Russia
Drinkman was arrested in the Netherlands in June 2012 at the request of the United States, along with Smilyanets.
While Smilyanets cooperated with U.S. authorities and arrived in the United States a few months after his arrest, Drinkman fought his extradition for more than a year.
Ultimately, Drinkman pleaded guilty in 2015 and was sentenced to 12 years in prison, including time served since his arrest. It is one of the harshest sentences given to a Russian hacker.
Drinkman served a total of 10 years and four months, or 86 percent of his sentence. U.S. federal prisoners earn credit each year for good behavior and typically serve 85 percent of their sentence. Smilyanets was sentenced to just time served, or less than six years, and currently resides in the United States, where he works as a cyber threat intelligence analyst.
Read More: