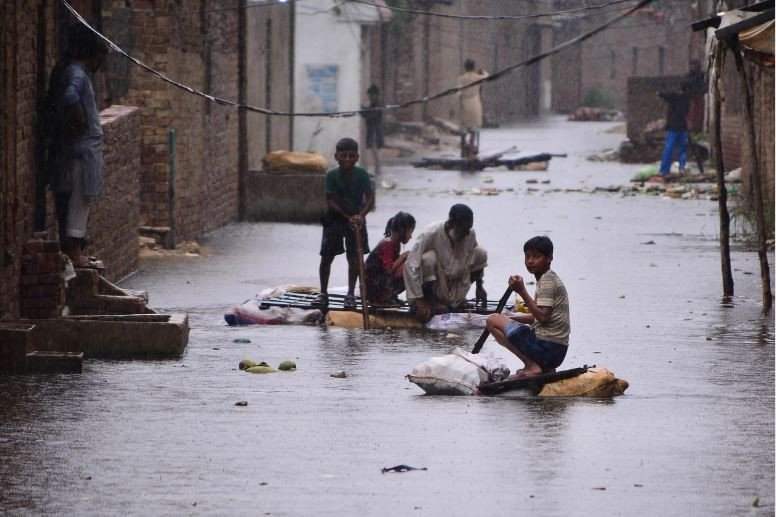
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR) issued a statement on 21 September (Yesterday) and its experts urged the government and other flood-fighting organizations and NGOs to invest in cost-effective floodwater purification filters developed by the Pakistan Council of Research Water Resources (PCRWR) that used modern technical equipment and helpful in mitigating water shortage and health issues due to stagnant water in flood affected areas. PCRWR claims that this is the cheapest and the most effective solution to the problem faced by flood-affected areas.
The PCRWR has built many portable water filtration plants since the flood hit the streets of Pakistan. As most of the water storage resources are either destroyed or the water in it is ruined. In the upcoming days, there is going to be a huge problem to provide drinking water to the refugees of the flood even if they are to successfully move to camps and habituated. The water filtration plants that PCRWR made used only solar power and manual mechanism based on the area needs and population capacity to handle the equipment so the supply of electricity isn’t going to be a problem. The solar water purification filter had a solar panel plate of almost 280watts used to provide power to run the suction machine to supply flood water to the purification filters.
The PCRWR filters effectively capture turbidity, mud, microbes, E.coli, and bacteria, while providing a cost-effective and local solution to provide instant and maximum relief to the flood-impacted masses. However, the purification plant had three main filters of varying capacity to remove bacterium and contaminants from the floodwater through three-prong cleansing, he added. The Solar based filter could purify 1,500 liters of floodwater per hour. However, the manual filter as compared to the solar-based only had a PLP wheel and a handle attached to it for drawing water into the filters whereas the rest of the technology was the same. This manual filter could purify 1,200 liters of contaminated water per hour, the officials said;
“The manual water filter costs Rs 1lac whereas the solar-based filter worth Rs 3 lac which is nominal for non-governmental organizations and philanthropists to donate for flood affected population,”
Prior to this statement by PCRWR, last month, a team of Danish experts also arrived in Pakistan to set up emergency water purification plants for climate refugees after floods inundated more than half the country. At a press briefing at his residence in Islamabad, Jakob Linulf Ambassador-designate of Denmark said;
“Our advanced emergency team from Denmark will leave for Sindh where it will establish its base to install and operate the water purification facility,”
On behalf of the Danish minister of foreign affairs as well as the Danish minister for development cooperation, Mr. Linulf paid his apologies and sorrow to all the affected people by the flood and the ones that died from it.
“Our thoughts are with their relatives and the many affected and displaced here in Pakistan, approximately 33 million people,” he said.
When the UN’s humanitarian flash appeal for Pakistan was raised, Denmark also supported $1.33 million to the UN Refugee Organisation, (UNHCR). This funding was provided in addition to Denmark’s core annual funding for UNHCR’s work in Pakistan and the region of $6.7 million. Thus Denmark has been Pakistan’s ally in these bad times from the start.
Later, on Aug 31, Denmark and Pakistan also signed a Green Framework Engagement, while on Aug 10, the two countries signed an agreement for Danish financing of sustainable infrastructure in Pakistan. Which gave a great chance for development to Pakistan and to excel in the infrastructure in flood-affected areas and even after that, the agreement includes other developmental infrastructure for Pakistan.
“These engagements will allow us to cooperate even more closely when it comes to green transition, sustainable development, and climate change mitigation. They will also assist in relation to rehabilitation and reconstruction,”
Read More: